DNS
This goes way more in-depth than the slides needs you to know
DNS Address Resolution
sequenceDiagram rect Cornsilk note right of Client: Internal DNS Resolution Client->>hosts file: www.smu.com? hosts file-->>Client: idk Client->>Internal DNS Cache: www.smu.com? Internal DNS Cache->>Client: idk end rect Bisque note right of Client: Recursive DNS Resolution Client->>ISP DNS 1: www.smu.com? ISP DNS 1->>+ISP DNS 2: www.smu.com? end rect LightSalmon note right of ISP DNS 2: Iterative DNS Resolution from Root ISP DNS 2->> Root Name Server: www.smu.com? Root Name Server->>ISP DNS 2: Ask the TLD at c.c.c.c ISP DNS 2->>TLD(.com): www.smu.com? TLD(.com)->>ISP DNS 2: Ask the Authoritative DNS at y.y.y.y ISP DNS 2->>Authoritative DNS: www.smu.com? Authoritative DNS->>ISP DNS 2: 8.8.8.8 end rect Bisque ISP DNS 2-->>ISP DNS 2: Update Cache ISP DNS 2->>-ISP DNS 1: 8.8.8.8 ISP DNS 1-->>ISP DNS 1: Update Cache ISP DNS 1->>Client: 8.8.8.8 end Client-->>Internal DNS Cache: Update Cache
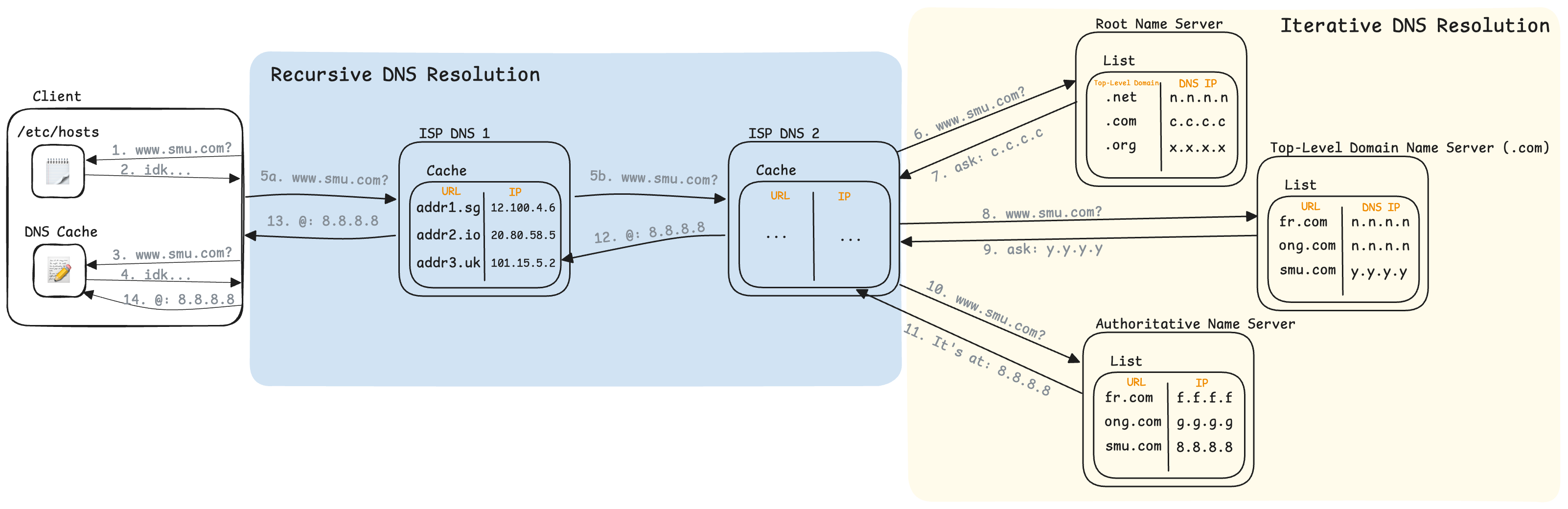
- Client checks its own hosts file for the address translation
- www.smu.com was not in the hosts file
- Client checks its own DNS Cache for the address translation
- www.smu.com was not in its own DNS Cache
- a) Client asks the default DNS server (configured by its ISP) for www.smu.com
- b) ISP DNS 1 did not have www.smu.com in its cache, recursively asks ISP DNS 2
- ISP DNS 2 did not have www.smu.com in its cache, so it asks one of the Global Root Name Servers
- The Root Name Server then replies with the address of a TLD Name Server which knows where all of the “.com” domains can be found
- ISP DNS 2 then asks the given TLD Name Server where to find www.smu.com
- The TLD Name Server then replies with the address of an Authoritative Name Server which knows where www.smu.com is
- ISP DNS 2 then asks the Authoritative Name Server where to find www.smu.com
- The Authoritative Name Server then replies with the IP address of www.smu.com
- ISP DNS 2 then updates its cache and forwards the IP address back to ISP DNS 1
- ISP DNS 1 then updates its cache and forwards the IP address back to the Client
- Client then updates its internal DNS cache
Recursive vs Iterative
In a recursive DNS query, if the DNS server that was asked does not know the address, it will ask another DNS server
In an iterative DNS query, if the DNS server that was asked does not know the address, it responds with the address of another DNS server. The sender then has to make another query to the given DNS server.